If you are building your own machine, you’ll surely have to make a decision between a 12V or 24V 3D printer. One has many advantages over the other, and we’ll try to explain why in this small guide.
Of course, other voltages exist such as 36V and 48V. We’ll also cover where these could be used.
Smaller wires
For delivering the same amount of power, a higher voltage means a lower current. This gives you the opportunity to use smaller wires for the same job. Check the table for more details regarding the current requirements.
| Power | Voltage | Current |
|---|---|---|
| 48W | 12V | 4A |
| 48W | 24V | 2A |
You can see that the voltage is inversely proportional to the current, meaning that a higher voltage means a lower current. But what does that means in term of wire size? Let’s check first how a conductor size influences the current that can pass through it.
Calculating the wire size
There are very simple rules guiding on the wire size:
- A higher section area (bigger wire) will have less resistance per unit of length
- The lesser the resistance, the lesser the losses
- The lesser losses, the lesser the temperature increase
Based on your wire material, a higher temperature can be tolerated. However, for a general consumer electronic device such as a 3D printer, you don’t want to keep your wires too hot. Considering heat and convection cooling from the wires can get complicated quickly.
As a general rule of thumb, a value ranging from 1% up to 3% can be used as the losses in a wire.
Taking our previous example, our 48W heater could use a cable with a loss ranging from 0.48W up to 1.44W.
Considering a loss of 0.48W (1%) over 1 meter of wire, the sizes shown in the table below should be used.
| Voltage | Wire size |
|---|---|
| 12V | 1.5mm² |
| 24V | 0.5mm² |

Bottom Line
In term of wire size, 24V has definitely an advantage over 12V, as the wires can be much smaller.
As there is generally no difference between a power supply of 300 watts running at 12V or 24V, you will save on your cables. If you are building your 3D printer, you’ll realize that you’ll need a lot of cables for your connections. This might not seem like it, but this is a great plus.
Reduce wiring costs
Makes cable management easier
Higher Motor Speed
Steppers are a bit confusing because of their rating. Most of them are usually rated at a very low voltage, often below 3V. Despite these ratings, they can be run at about any voltage. The secret lies in the stepper motor drivers.
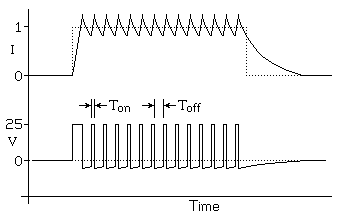
Current Chopper
The stepper drivers use the high inductive load from a stepper motor to drive it at any voltage. The slow voltage rise enables the driver to cut the supply voltage at a certain point is reached. The voltage then starts to decay.
Successively controlling the voltage enables to set the current at a precise value, no matters the input voltage.
Bottom Line

In term of motor speed, 24V has again an advantage over 12V.
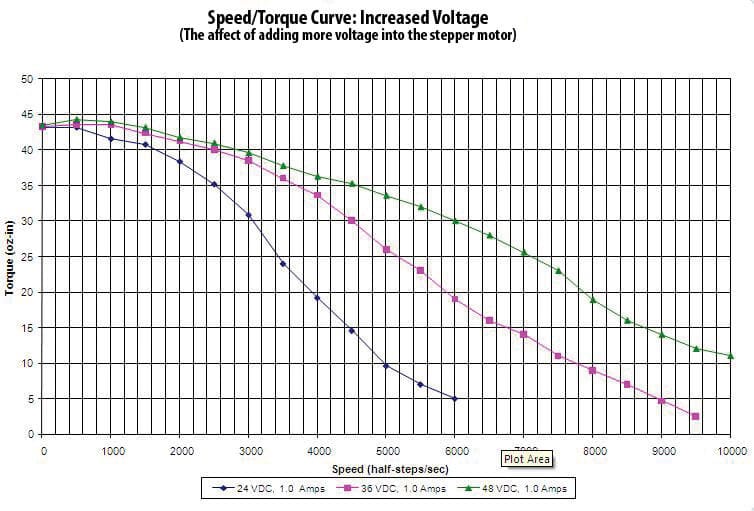
Some specialized external stepper drivers, such as the DM422 and DM556, will benefit from having a higher voltage than 24V. This is where a power supply of 36V or 48V can be useful. These are usually used for bigger motors than NEMA17, such as NEMA23.
However, most 3D printer controllers won’t be compatible with such high voltage when the stepper drivers are integrated. Most RAMPS and Arduino are rated only for 12V. There are some well-designed boards that can accept a higher voltage. For example, the Panucatt Azteeg X5 GT is rated at 30V for main input and 35V for stepper input.
Higher RPM
Greater Torque
Higher Heating Power
Most heater cartridges are generally 6mm in diameter and around 20mm in length. There is a limit in power density to these cartridges. In other words, this small size can’t be as powerful as you’d like.
In 12V, it’s hard to get anything over 45W. Reliability will be a big problem and MTBF will be reduced greatly.
In 24V, it’s possible to go a little higher in terms of power density. For the same size, 60W can be easily done.
Fast Heating
Having a higher heater power has advantages and disadvantages.
Your hotend will heat up more quickly. In general applications, this isn’t a big advantage. However, if you have multiple extruders on the same carriage, you might want to reduce the temperature when the head is not being used. Having a faster heater can greatly reduce heating time.
Having a powerful heater can help you reach a higher temperature. The convection losses increase with the hotend temperature. At a certain point, there is not enough power to raise the block temperature and compensate for the losses in free air. Most 12V heaters will have a hard time reaching 400°C and then will drop as soon as the head moves or filament is pushed through.
The drawback with faster heating is that it is harder to fine tune. Some modifications to the firmware might be required in order to reduce overshoot and stabilize the temperature.
Bottom Line
In term of heating, 24V has more advantages.
You’ll be able to have more heating power, heat faster, and reach higher temperatures. Make sure to configure your firmware properly and you’ll be good to go.
Higher Heating Power
Higher Temperature
Parts Availability
The main disadvantage of having a 24V system is the part availability in this voltage. It is much easier to find components that run in 12V when you need them in small quantity.
Fans are probably the easiest to get in 24V.
Pumps, however, are quite often used in computer liquid cooling systems. These runs at 12V. 24V pumps are rare.
Lights kits are also more common in 12V.
DC-DC Step Down
Adding a second power supply or adding a step-down is very common in 3D printers. For example, the Arduino has a built-in DC-DC converter to output 5V.
Some machines have 5V, 12V and 24V power supplies to separate motors, general electronics, and logic voltages. It’s up to you to determine the best solution if you want/need to use many different voltages.

Bottom Line
This time, 12V has more advantages.
It’s much easier to get the parts for 12V. Nothing is wrong with having two different power supplies running in your system, or having a DC-DC converter. It’s up to you to decide what’s best for your system.
Hard to supply parts
Need a second power supply
Conclusion
As you have seen, there are many advantages to having a 24V 3D printer. You’ll get better heating and motor performance, and also reduce your wiring costs.
However, depending on your component choices and suppliers, getting some parts in 24V might be tricky.
You can quickly solve this by simply adding a DC-DC converter or a second power supply to power 12V.
Thanks!
Thanks for reading. I hope you have learned new stuff. Do not hesitate if you have any question or if you have seen something wrong in this blog.